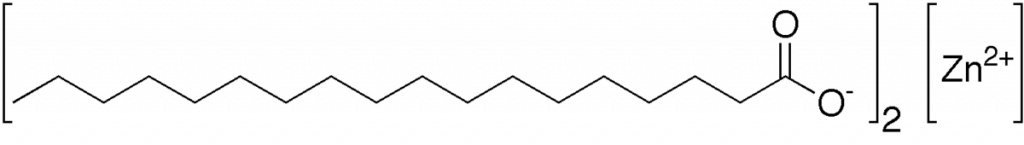
Zinc stearate, with its chemical formula Zn(C₁₈H₃₅O₂)₂, is a zinc soap of stearic acid. It is a white, powdery substance that is water repellent. Lending to its myriad of uses across various industries, from the manufacturing of rubber and cosmetics to its pivotal role in the food sector. In the context of the food industry, zinc stearate emerges as a rather specialized additive. This article delves into the various applications, utility, and the implications of using zinc stearate in the food processing sphere.
Applications and Uses in the Food Industry
- Release Agent:. One of the primary roles of zinc stearate in the food industry is its function as a release agent. Due to its water-repellent properties, it ensures that food does not stick to machinery, molds, and other surfaces. This is especially useful in confectionery manufacturing, where candies, chocolates, and other sweets are molded into various shapes.
- Anti-Caking Agent: In food products like spices, powdered condiments, and other dry mixes, zinc stearate acts as an anti-caking agent. It prevents the particles from sticking together, ensuring the mix remains free-flowing.
- Food Fortification:. Zinc is an essential mineral for the human body, aiding in processes like immune response, DNA synthesis, and cell division. Some foods are fortified with zinc to ensure that the consumers get the required amount of this essential nutrient, and zinc stearate serves as a source.
Safety and Regulatory Status
Ensuring that additives are safe for consumption is paramount. For zinc stearate, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have set an acceptable daily intake. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies zinc stearate as a substance that is “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) when consumed in moderate quantities.
However, as with all food additives, the key lies in moderation. Overconsumption or prolonged intake of large amounts can lead to an excessive intake of zinc. Leading to adverse health effects such as nausea, vomiting, and other gastrointestinal issues.
Implications of Using Zinc Stearate in the Food Industry
- Environmental Considerations:. The production of zinc stearate, like many industrial processes, can have environmental impacts, particularly concerning the mining of zinc. Responsible sourcing and manufacturing practices become essential to minimize environmental harm.
- Ethical and Health Concerns:. As with any additive, there’s a debate about the necessity and potential health implications of its use. Some health-conscious consumers might prefer products that don’t use such additives. Therefore, brands using zinc stearate may face challenges in catering to this demographic.
- Economic Implications: The use of additives can both increase and decrease production costs. While zinc stearate can increase the shelf life and improve the texture of products. It also adds an additional component to the manufacturing process. Balancing these costs with consumer demand and willingness to pay is a constant challenge for manufacturers.
Zinc stearate, with its unique properties, has carved out a niche for itself in the food industry. While its use simplifies certain production processes and ensures a certain quality and consistency in products, there are also concerns and implications to consider, from health to environmental.
As consumers become more educated and discerning about what goes into their food, transparency, responsible sourcing, and clear communication from food manufacturers will become even more crucial. In the end, while zinc stearate serves a practical purpose, its use, like all food additives, needs to be balanced with the broader concerns of health, environment, and consumer preferences.
