Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid, has become indispensable in a diverse array of industrial and consumer applications. Indeed, this versatile compound is ubiquitous, found in everything from cosmetics and food to rubber and candles. To fully appreciate its significance, it’s crucial to understand both its molecular structure and its wide range of uses. In the sections below, we will delve into the structure, properties, and common usages of stearic acid, thereby offering a comprehensive overview.
Molecular Structure (Stearic Acid Structure and Properties)
Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2. Its IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. Structurally, it consists of an 18-carbon chain attached to a carboxylic acid group at one end. Being a saturated fatty acid, all carbon atoms are connected by single bonds, making it a linear, long-chain structure. The absence of double bonds in the carbon chain contributes to its stability and higher melting point compared to unsaturated fatty acids.
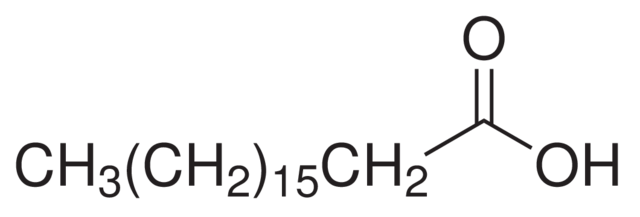
Physical and Chemical Properties (Stearic Acid Structure and Properties)
Melting and Boiling Points
Stearic acid has a melting point of 69.6 degrees Celsius and a boiling point of 361 degrees Celsius. Its higher melting point compared to unsaturated fatty acids makes it solid at room temperature.
Solubility
It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether.
Stability
Stearic acid is stable under standard conditions but can react with strong oxidizing agents. Its saturated structure makes it less prone to oxidation and rancidity.
Common Uses (Stearic Acid Structure and Properties)
Cosmetics and Personal Care
Stearic acid is a key component in soaps, lotions, and shampoos. It acts as an emollient and a thickening agent, providing texture and stability to the product.
Food Industry
Also used as a food additive, often coded as E570. It serves as an emulsifier in processed foods like baked goods and candies.
Industrial Applications
In industries like rubber and plastics, stearic acid serves as a release agent, helping in the separation of the finished product from its mold.
Candles and Detergents
It is a vital ingredient in the manufacture of candles, providing rigidity and longer burn time. In detergents, it acts as a surfactant, improving cleaning efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Due to its widespread use, there is ongoing research on its environmental impact. Currently, it is not considered a significant environmental hazard.
Conclusion
Stearic acid, distinguished by its unique molecular structure, offers a multitude of applications that span from cosmetics to industrial manufacturing. Specifically, its saturated, long-chain structure contributes to its remarkable stability and versatility in various uses. Moreover, as research progresses, new applications and benefits continue to emerge, further cementing its status as a versatile and vital component across different sectors.
