Magnesium stearate is a common excipient in the pharmaceutical industry. Acting as both a lubricant and a binder, it’s an unsung hero in many of the medications we take. This article delves into the importance of magnesium stearate, its benefits, potential concerns, and the crucial role it plays in the pharmaceutical sector.
1. What is Magnesium Stearate?
Magnesium stearate is a magnesium salt of stearic acid. Chemically, it’s a white, water-insoluble powder. It’s not only found in pharmaceuticals but also in food products and cosmetics. Its primary function in tablet formulation is to prevent the individual ingredients from sticking to each other and to the machine during processing.
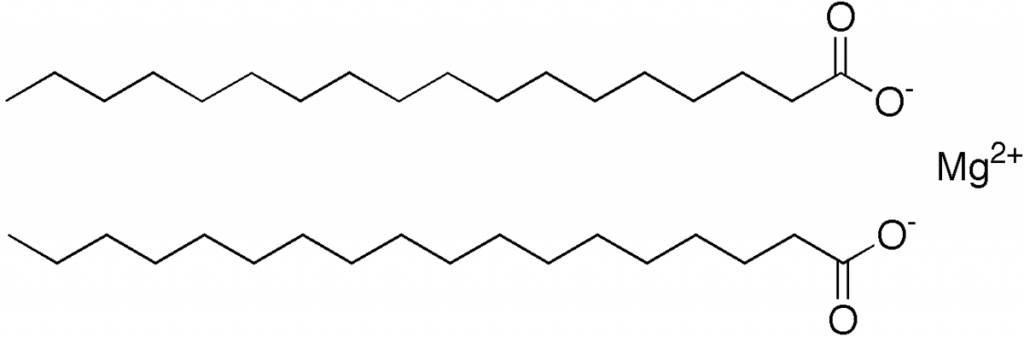
2. Why is Magnesium Stearate Used in Pharmaceuticals?
- Lubrication: It allows for efficient and consistent production of tablets and capsules. By reducing friction during the manufacturing process, it ensures that tablets don’t adhere to the machinery.
- Flowability: Magnesium stearate improves the consistency and flowability of the drug powder mixture, ensuring uniformity in tablet and capsule filling.
- Improved Dissolution: It can enhance the rate at which the tablet dissolves in the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring that the active ingredient is released efficiently.
3. Benefits Over Other Excipients (Magnesium Stearate in the Pharmaceutical Industry)
The pharmaceutical world is vast, with several alternatives available. Yet, magnesium stearate stands out due to:
- Cost-effectiveness: It provides an economical solution for the challenges faced during tablet compression.
- Versatility: Suitable for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic formulations.
- Safety: Classified as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) by the FDA, making it a preferred choice for many formulations.
While magnesium stearate is widespread, it’s not without its critics:
- Allergic Reactions: Rarely, some individuals might experience an allergic reaction to magnesium stearate, though these instances are infrequent.
- Digestive Disturbances: There have been sporadic reports of digestive disturbances, but these reports are inconclusive, and further research is necessary.
- Bioavailability: Concerns have been raised about magnesium stearate affecting the bioavailability of drugs, potentially inhibiting their absorption. However, these concerns have been largely debunked in multiple studies.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
With the rising emphasis on green chemistry and sustainable practices, the pharmaceutical industry is under scrutiny. Magnesium stearate typically originates from vegetable oils (like palm or cottonseed) or animal fats:
- Vegetable-Derived Magnesium Stearate: A sustainable choice, but there are concerns over deforestation when it comes to sources like palm oil.
- Animal-Derived Magnesium Stearate: Raises ethical considerations for vegetarians and vegans, and those concerned about animal welfare.
To address these concerns, companies are increasingly transparent about sourcing and are exploring sustainable alternatives.
Magnesium stearate, given its widespread usage, is under the purview of various regulatory bodies:
- FDA (U.S.): Classified as GRAS, meaning it’s safe for consumption in both food and pharmaceuticals.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA): Acknowledges its crucial role in drug formulations and has guidelines regarding its quantity and quality in medicines.
- World Health Organization (WHO): Recognizes magnesium stearate’s importance and has set guidelines for its use.
7. Future Outlook
With the pharmaceutical industry evolving, magnesium stearate’s role is bound to adapt:
- Innovation: Companies are continually researching to enhance its properties, making it more efficient and even more beneficial.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Efforts are underway to ensure that magnesium stearate production has a minimal environmental footprint.
Magnesium stearate remains an integral part of the pharmaceutical landscape. Its benefits in drug formulation are undeniable, and while concerns exist, they are outweighed by its advantages. As the industry progresses, it will be fascinating to see how this humble excipient evolves, ensuring that our medicines are effective, safe, and sustainable.
